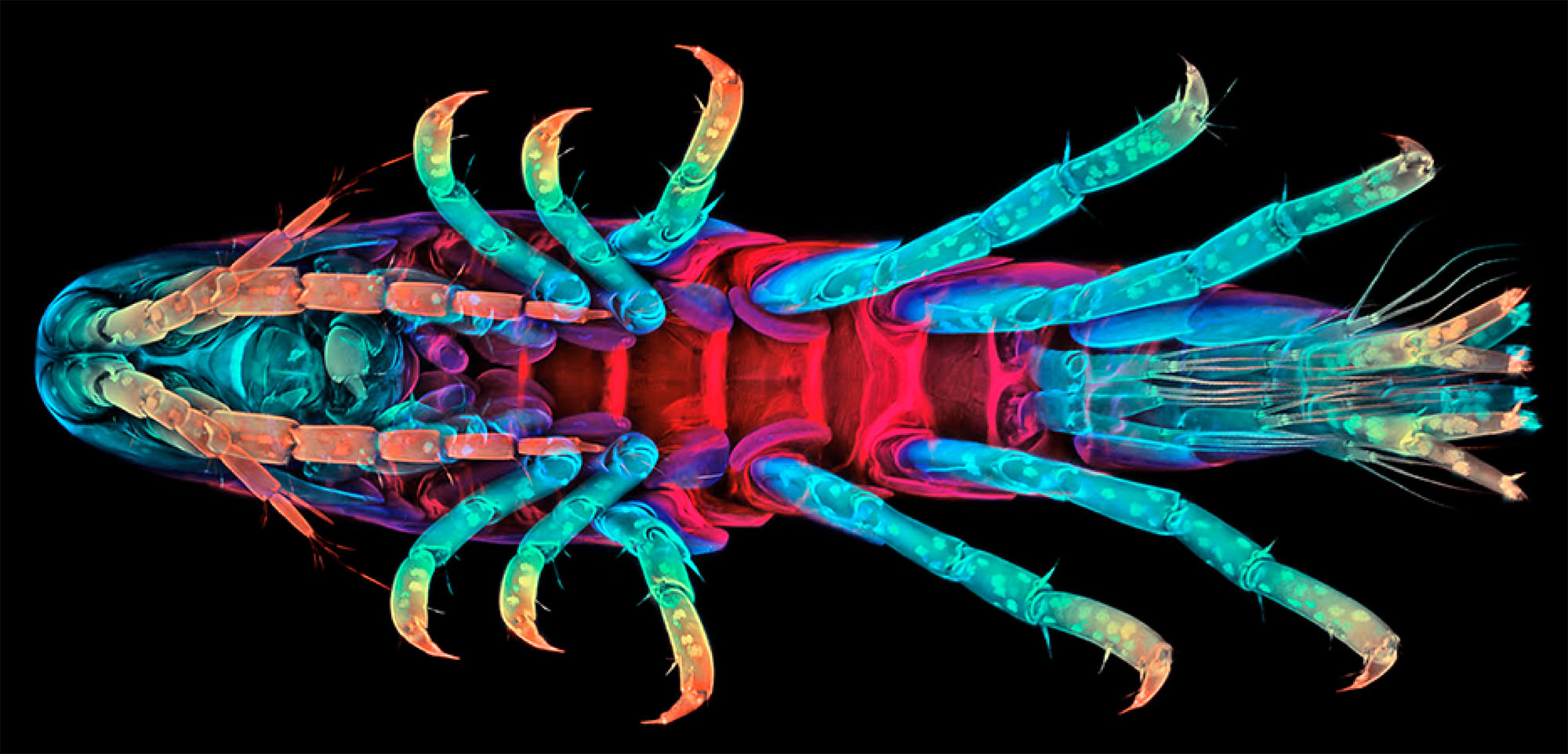

The crustacean amphipod Parhyale hawaiensis has emerged as an attractive experimental model to address longstanding questions in biology, including cell fate specification, segmentation, neurogenesis, organ morphogenesis and regeneration. This site provides comprehensive and easy access to all resources pertaining to Parhyale experimentation.
Parhyale genome
Contigs were assembled with Abyss at k-length of 70 and 120. Both K70 and K120 assemblies were merged with GAM-NGS. Scaffolding was done with SSPACE. Go here for an ipython notebook of the assembly process.
Scaffolds (.fasta)
Contigs (.fasta)
Annotations (.gff)
Parhyale transcriptome
Gene annotations were done with a combination of Evidence Modeler (EVM) and Augustus. EVM was first used to generate high-confidence predictions using ab initio predictions and transcriptome mapping. Augustus was then trained using these high confidence predictions. Read the first response to this post at BioStars for more detail. Go here for an ipython notebook of the annotation process.
Each gene has an ID in the format of "phaw_30_source_mapped_id". "Source" can either be from transcriptome (tra) or from Augustus gene predictions (aug). "Mapped" can either be unmapped (u) or mapped (m). For example: "phaw_30_tra_u.026676" means this gene is sourced from the transcriptome and does not map to the genome (due to incompleteness of the genome or transcriptome assembly error).
Genes - nucleotide (.fasta)
Genes - protein (.fasta)
Introduction to Parhyale and animal culture



Parhyale embryogenesis and early cell lineage




Dissection, fixation, antibody staining and hybridization of Parhyale embryos




Parhyale embryo microinjection and transgenesis





Parhyale blastomere ablation and isolation




CRISPR/Cas genome editing in Parhyale embryos



Parhyale embryo live imaging



Aziz Aboobaker lab
University of Oxford
Department of Zoology
South Parks Road
Oxford, UK OX13PS
Email aziz.aboobaker@zoo.ox.ac.uk
Web page http://aboobakerlab.com
Michalis Averof Lab
Institute of Functional Genomics Lyon (IGFL)
32-34 avenue Tony Garnier
Lyon 69007, France
Tel. +33-4-26731364
Email michalis.averof@ens-lyon.fr
Web page https://averof-lab.org/
Cassandra G. Extavour Lab
Harvard University
Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology
Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology
16 Divinity Avenue, BioLabs 2087
Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
Tel. Office 1 617 496 1935
Tel. Lab 1 617 496 0983/2984
Email extavour@oeb.harvard.edu
Web page http://www.extavourlab.com
Nipam H. Patel Lab
University of California, Berkeley
Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
525A LSA #3200
Berkeley, CA 94720-3200, USA
Tel. Office +1-510-643-4605
Tel. Lab +1-510-643-4201
Email nipam@berkeley.edu
Web pagehttp://www.patellab.org
Anastasios Pavlopoulos Lab
Janelia Research Campus
19700 Helix Drive
Ashburn, VA 20147, USA
Tel. +1-571-209-4000 (ext.3337)
Email pavlopoulosa@janelia.hhmi.org
Web page https://www.janelia.org/lab/pavlopoulos-lab
Carsten Wolff / Gerhard Scholtz Lab
Humboldt University
Department of Biology / Comparative Zoology
Philippstr. 13, Haus 2
10115 Berlin, Germany
Tel. +49-30-2093-6284
Email carsten.wolff@rz.hu-berlin.de
Web page https://www.biologie.hu-berlin.de/de/gruppenseiten/compzool